LOAD MORE
You're viewed 9 of 46 products
Daicel Pharma synthesizes more than twenty-five high-quality Somatostatin impurities, such as D-Ala(1)-Somatostatin, D-Asn(5)-Somatostatin, D-Cys(3)-Somatostatin, D-Lys(4)-Somatostatin, D-Phe(6)-Somatostatin, D-Cys(14)-Somatostatin, [3-14]-Somatostatin, Di-Trp(8)-Somatostatin, Endo [Ser-Cys(Acm)]-Somatostatin, and more, crucial in determining the quality, stability, and biological safety of the active pharmaceutical ingredient, Somatostatin. Moreover, Daicel Pharma offers custom synthesis of Somatostatin impurities and delivers them globally.
Somatostatin [CAS: 51110-01-1] is a tetradecapeptide that helps regulate neuroendocrine functions. It produces in several areas of the human body, including the hypothalamus, central nervous system, gastrointestinal tract, and pancreas. It is also known as the growth hormone release inhibiting factor.
Somatostatin inhibits endocrine, exocrine, pancreatic, pituitary, and GI secretions. It prevents angiogenesis. Due to its short half-life, Somatostatin analogs in stable forms help to treat neuroendocrine tumors (NET). Synthetic analogs of Somatostatin, including lanreotide, octreotide, seglitide, and vapreotide, have been developed to manage various diseases like acromegaly and neuroendocrine tumors, including glucagonoma, carcinoid tumors, gastrinoma, Somatostatinoma, growth hormone releasing factor tumor (GRFoma), VIPoma, insulinoma, many pituitary adenomas, and pheochromocytoma.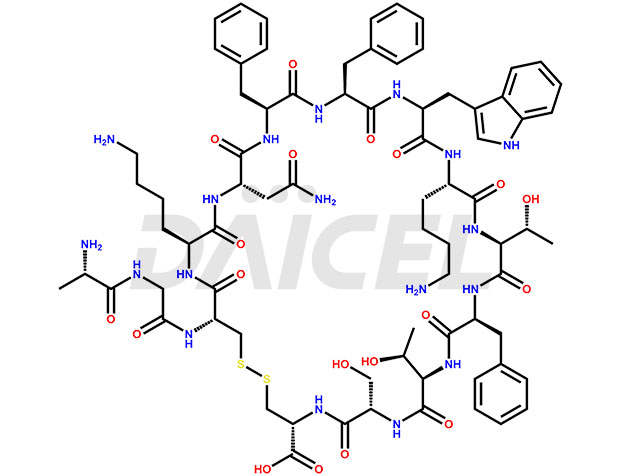
The chemical formula for Somatostatin is C76H104N18O19S2, and its molecular weight is approximately 1637.9 g/mol.
Somatostatin’s regulatory effect is due to its ability to bind to six different receptors in various systems and cells of the body. They are known as G-protein coupled receptors (GPCR), specific to Somatostatin. Once activated, these receptors decrease intracellular cyclic AMP and calcium and increase potassium currents, causing a decrease in hormone secretion of the target tissue.
Somatostatin impurities are of different types, including truncated, N-terminal modified, and oxidized peptides. Truncated peptides can occur during Synthesis1 due to incomplete reactions, leading to peptides with missing amino acids. N-terminal modified peptides can arise from the purification process, where some amino acids are added or removed. Oxidized peptides can be formed by exposure to oxidizing agents or air, like oxidized Somatostatin impurities or disulfide-linked homodimers. Some of these impurities can be harmful and may cause adverse effects if injected into a patient. Therefore, it is crucial to minimize contaminants during synthesis and purify2 and analyze the drug to ensure it is safe and effective.
Daicel offers a Certificate of Analysis (CoA) from a cGMP-compliant analytical facility for more than twenty-five Somatostatin impurity stndards, including D-Ala(1)-Somatostatin, D-Asn(5)-Somatostatin, D-Cys(3)-Somatostatin, D-Lys(4)-Somatostatin, D-Phe(6)-Somatostatin, D-Cys(14)-Somatostatin, [3-14]-Somatostatin, Di-Trp(8)-Somatostatin, Endo [Ser-Cys(Acm)]-Somatostatin, and more. The CoA includes complete characterization data, such as CHN, Amino Acid composition and Sequence Analysis, MASS, and HPLC purity. We also give a characterization report on delivery.
Daicel has the technology and expertise to prepare any unknown Somatostatin impurity or degradation product. The company also provides labeled compounds to quantify the efficacy of generic Somatostatin. Daicel offers highly pure isotope-labeled standards of Somatostatin for bioanalytical research and BA/BE studies with the percentage of isotope data in CoA.
The common impurities found in Somatostatin include truncated Somatostatin peptides, oxidized Somatostatin, and N-terminal modified Somatostatin.
The Common impurities found during Somatostatin synthesis include incomplete coupling of amino acids, racemization of amino acids, and deletion sequences in the final peptide.
Somatostatin impurities are detected using analytical techniques such as high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC), liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry (LC-MS), etc.
Somatostatin impurities may be removed from the drug by various purification techniques such as HPLC, size exclusion chromatography, and reverse-phase chromatography.
Note: Products protected by valid patents by a manufacturer are not offered for sale in countries having patent protection. The sale of such products constitutes a patent infringement, and its liability is at the buyer's risk.