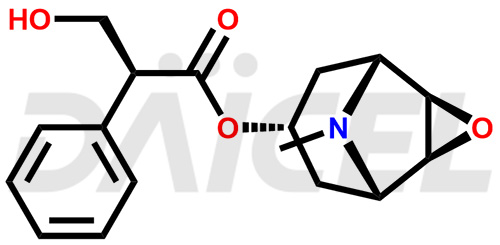
Scopolamine
General Information
Scopolamine Impurities and Scopolamine
Daicel Pharma is a reliable source for synthesizing high-quality Scopolamine impurities, like Hysocine Butylbromide EP Impurity E, N-Desmethyl scopolamine, and Scopolamine Enantiomer. These impurities help assess the quality, stability, and safety of the active pharmaceutical ingredient, Scopolamine. Daicel Pharma also offers custom synthesis of Scopolamine impurities, which can be shipped worldwide to meet customers’ unique requirements.
Scopolamine [CAS: 51-34-3] is an FDA-approved drug classified as an anti-muscarinic and anti-cholinergic drug that acts as a competitive antagonist of muscarinic acetylcholine receptors.
It prevents and treats motion sickness, including nausea, vomiting, and dizziness associated with travel or specific medical procedures.
Scopolamine: Use and Commercial Availability
Scopolamine is an inhibitor of muscarinic receptors. It is also hyoscine that helps prevent and treat motion sickness symptoms, such as nausea, vomiting, and dizziness. It also manages irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) symptoms and alleviates excessive sweating and drooling. Scopolamine is commercially available as transdermal patches, tablets, and injections.
Scopolamine is available under Transderm Scop, which effectively contains the active ingredient, Scopolamine.
Scopolamine Structure and Mechanism of Action 
The chemical name of Scopolamine is (αS)- α-(hydroxymethyl)-, (1α,2β,4β,5α,7β)-9-methyl-3-oxa-9-azatricyclo[3.3.1.02,4]non-7-yl ester Benzeneacetic acid. Its chemical formula is C17H21NO4, and its molecular weight is approximately 303.35 g/mol.
Scopolamine blocks cholinergic transmission from the vestibular nuclei to higher centers in the Central nervous system. It prevents saliva and sweat secretion, reduces gastrointestinal secretions and gut motility, and causes drowsiness.
Scopolamine Impurities and Synthesis
The formation of impurities is possible throughout the manufacturing process of Scopolamine, which can compromise its efficacy or pose risks to patients. They can originate from different sources, including starting materials, intermediates, and reagents utilized in synthesizing Scopolamine. Consequently, it becomes crucial to strictly control and monitor these impurities to guarantee the drug’s safety and effectiveness.
Daicel offers a Certificate of Analysis (CoA) from a cGMP-compliant analytical facility for Scopolamine impurity standards. The CoA includes complete characterization data, such as 1H NMR, 13C NMR, IR, MASS, and HPLC purity1,2. We also provide 13C-DEPT on request. Upon delivery, we also give a complete characterization report. Daicel has the technology and expertise to prepare any unknown Scopolamine impurity or degradation product. We also provide labeled compounds. Daicel offers a deuterium-labeled standard of Scopolamine, Scopolamine D3 HCl, for bioanalytical research and BA/BE studies.
References
FAQ's
References
- Solomon, Mark J.; Crane, Frank A.; Chu, B. L. Wu; Mika, E. S., Simultaneous quantitative gas-chromatographic determination of atropine and scopolamine, Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences, Volume: 58, Issue: 2, Pages: 264-6, 1969
- Chu, B. L. Wu; Mika, Edward S., Use of tetraphenylethylene in quantitative GLC [gas-liquid chromatography] of hyoscyamine and scopolamine, Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences Volume: 59, Issue: 10, Pages: 1508-10, 1970, DOI: (https://doi.org/10.1002/jps.2600591034)
Frequently Asked Questions
Are Scopolamine impurities harmful?
The existence of impurities does not always signify danger as long as their nature and levels are under strict control. The setting of impurity levels is based on safety and efficacy considerations. Impurity levels must be within acceptable range to reduce potential adverse effects.
Can impurities in Scopolamine affect its effectiveness?
Impurities in Scopolamine can affect its effectiveness by altering the drug's pharmacokinetics, pharmacodynamics, or stability. Manufacturers aim to control impurities so the drug maintains its potency and delivers the desired therapeutic outcomes.
How are Scopolamine impurities detected and quantified?
Analytical techniques such as high-performance liquid chromatography with ultraviolet detection help detect and quantify Scopolamine impurities. These methods enable accurate identification and measurement of impurity levels.
What are the temperature conditions required to store Scopolamine Impurities?
Scopolamine Impurities should be stored at a controlled room temperature between 2-8°C or as indicated on the Certificate of Analysis (CoA).
Note: Products protected by valid patents by a manufacturer are not offered for sale in countries having patent protection. The sale of such products constitutes a patent infringement, and its liability is at the buyer's risk.