Nelarabine
General Information
Nelarabine Impurities and Nelarabine
Daicel Pharma is a trusted provider of quality Nelarabine impurity standards, including 2,6-Diaminopurine arabinoside, 9-(Beta-d-arabino furanosyl) Guanine, Nelarabine Alpha isomer impurity, Nelarabine impurity 17, and Nelarabine Stage-1 Impurity. These impurities are critical in determining the active pharmaceutical ingredient Nelarabine’s quality, stability, and biological safety. Additionally, Daicel Pharma can synthesize Nelarabine impurities according to precise customer specifications while guaranteeing worldwide delivery.
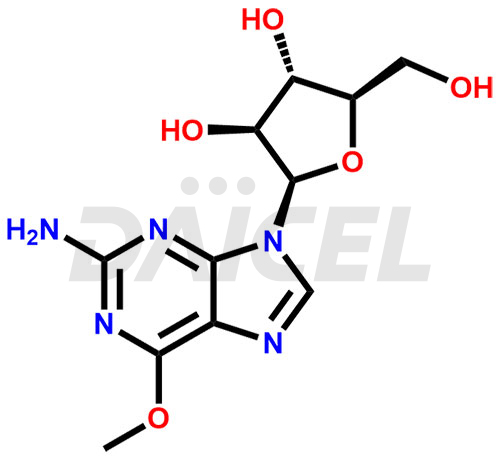
Nelarabine [CAS: 121032-29-9] is a pro-drug of the deoxyguanosine analog, 9-β-Darabinofuranosylguanine (ara-G). It treats patients diagnosed with T-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia (T-ALL) and T-cell lymphoblastic lymphoma (T-LBL) who have not shown a response to or have experienced a relapse after undergoing at least two chemotherapy regimens.
Nelarabine: Use and Commercial Availability
Nelarabine treats T-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia, a rare type of non-Hodgkin lymphoma primarily affecting lymph nodes. It is for patients who have not responded to or have relapsed following treatment with at least two chemotherapy regimens. Nelarabine helps in targeting and killing these cancer cells.
Nelarabine is available under the brand name, Arranon active ingredient Nelarabine.
Nelarabine Structure and Mechanism of Action 
The chemical name of Nelarabine is 9-β-D-Arabinofuranosyl-6-methoxy-9H-purin-2-amine. Its chemical formula is C11H15N5O5, and its molecular weight is approximately 297.27 g/mol.
Nelarabine is converted to the active 5’-triphosphate, ara-GTP, after demethylation by adenosine deaminase (ADA). Nelarabine inhibits DNA synthesis and cell death after ara-GTP accumulation in leukemic blasts.
Nelarabine Impurities and Synthesis
Nelarabine impurities can arise during synthesis1 due to the storage or use of specific raw materials and intermediates in manufacturing. These impurities encompass related compounds, degradation products, and process impurities. Stringent quality control measures and analytical methods are crucial to ensure the purity and safety of Nelarabine for patient use.
Daicel Pharma provides a comprehensive Certificate of Analysis (CoA) for Nelarabine impurity standards, such as 2,6-Diaminopurine arabinoside, 9-(Beta-d-arabino furanosyl) Guanine, Nelarabine Alpha isomer impurity, Nelarabine impurity 17, and Nelarabine Stage-1 Impurity. The CoA includes detailed characterization data such as 1H NMR, 13C NMR, IR, MASS, and HPLC purity2. Additionally, upon delivery, a complete 13C-DEPT is also provided. Daicel Pharma possesses the technology and expertise to synthesize any unknown Nelarabine impurity or degradation product.
References
FAQ's
References
- Krenitsky, Thomas Anthony; Koszalka, George Walter; Jones, Lynda Addington; Averett, Devron Randolph; Moorman, Allan Ray, Antiviral compounds, Wellcome Foundation Ltd., United Kingdom, EP294114B1, September 11, 1996
- Liu, Xingling; Li, Sanwang; Cheng, Zeneng; Cheng, Hang; Liu, Zhi; Guo, Xin; Xie, Feifan; Yu, Peng, Simultaneous Determination of Nelarabine and Its Active Metabolite 9-β-D-Arabinofuranosylguanine (Ara-G) in Human Plasma, Chromatographia, Volume: 77, Issue: 1-2, Pages: 91-97, 2014
Frequently Asked Questions
How are Nelarabine impurities detected and quantified?
Analytical methods, such as high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC), are commonly used to detect and quantify impurities in Nelarabine batches.
How are specifications determined for Nelarabine impurities?
The specifications for Nelarabine impurities are determined through meticulous research, analysis, and adherence to regulatory guidelines.
How do chromatographic methods help in the chiral separation of Nelarabine Impurities?
Several chromatographic techniques can help in chiral separation, including high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC). These methods utilize chiral stationary phases (CSPs) to selectively retain and separate the enantiomers based on their interactions with the stationary or mobile phase.
What are the temperature conditions required to store Nelarabine impurities?
Nelarabine impurities should generally be stored at a controlled room temperature between 2-8 ⁰C or as indicated on the Certificate of Analysis (CoA).
Note: Products protected by valid patents by a manufacturer are not offered for sale in countries having patent protection. The sale of such products constitutes a patent infringement, and its liability is at the buyer's risk.