LOAD MORE
You're viewed 9 of 17 products
For evaluating the purity and safety of Linagliptin, an essential active pharmaceutical ingredient, Daicel Pharma offers a customized synthesis of Linagliptin impurity standards. These impurity standards include crucial compounds such as 8-Bromo-3-methyl-7-(2-butynyl)-xanthine, Linagliptin impurity E, Linagliptin Methyldimer, Linagliptin N-glucose impurity, Linagliptin Nitroso impurity’s internal STD, Linagliptin S-isomer, N-Acetyl Linagliptin, N-Boc Linagliptin, N-Carbamoyl Linagliptin, and N-Formyl Linagliptin. Additionally, Daicel Pharma provides worldwide delivery options for Linagliptin impurity standards.
Linagliptin [CAS: 668270-12-0], a potent dihydropurinedione-based inhibitor of dipeptidyl peptidase 4 (DPP-4), is orally bioavailable and exhibits hypoglycemic activity. It treats type 2 diabetes in combination with diet and exercise alone or with other oral hypoglycemic agents.
Linagliptin, marketed under Tradjenta, treats type 2 diabetes mellitus to improve glycemic control in adults. It acts as a monotherapy in patients inadequately controlled by diet and exercise alone and for whom metformin is unsuitable or contraindicated due to renal impairment.
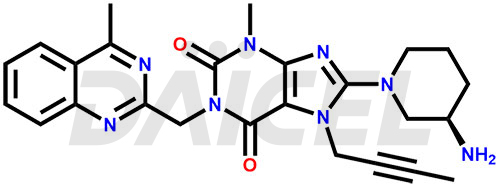
The chemical name of Linagliptin is 8-[(3R)-3-Amino-1-piperidinyl]-7-(2-butyn-1-yl)-3,7-dihydro-3-methyl-1-[(4-methyl-2-quinazolinyl)methyl]-1H-purine-2,6-dione. Its chemical formula is C25H28N8O2, and its molecular weight is approximately 472.5 g/mol.
Linagliptin degrades the incretin hormone, glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1). It stimulates insulin release in a glucose-dependent manner and decreases glucagon levels in circulation.
Linagliptin impurities refer to unintended substances that may be present in Linagliptin formulations. They can originate from manufacturing1, raw materials, or storage conditions. Their presence can potentially affect its purity, potency, and overall quality. Rigorous quality control measures by pharmaceutical manufacturers help ensure the safety and efficacy of the medication. These measures include thorough testing and analysis to identify and quantify impurities and strict adherence to regulatory guidelines and standards. By controlling impurity levels within acceptable limits, pharmaceutical companies strive to provide patients with high-quality Linagliptin formulations for treating type 2 diabetes mellitus, minimizing any potential risks associated with impurities.
Daicel Pharma strictly adheres to cGMP standards and operates an analytical facility for preparing Linagliptin impurity standards, which include 8-Bromo-3-methyl-7-(2-butynyl)-xanthine, Linagliptin impurity E, Linagliptin Methyldimer, Linagliptin N-glucose impurity, Linagliptin Nitroso impurity’s internal STD, Linagliptin S-isomer, N-Acetyl Linagliptin, N-Boc Linagliptin, N-Carbamoyl Linagliptin, and N-Formyl Linagliptin. Our Linagliptin impurity standards have a detailed Certificate of Analysis (CoA) that provides a comprehensive characterization report. This report includes data obtained through techniques,1H NMR, 13C NMR, IR, MASS, and HPLC purity analysis2. Upon request, we give additional data like 13C-DEPT. Moreover, we can synthesize unknown Linagliptin impurity standards and degradation products. Each delivery has a comprehensive characterization report.
Regulatory guidelines outline the necessary documentation and reporting of Linagliptin impurities to ensure transparency and accountability.
Genotoxicity testing is typically conducted to assess the potential of Linagliptin impurities to cause DNA damage or mutations.
Improper manufacturing processes, such as poor handling or contamination, can contribute to the formation of impurities in Linagliptin.
Linagliptin impurities should be stored at a controlled room temperature, usually between 2-8 °C.
Note: Products protected by valid patents by a manufacturer are not offered for sale in countries having patent protection. The sale of such products constitutes a patent infringement, and its liability is at the buyer's risk.