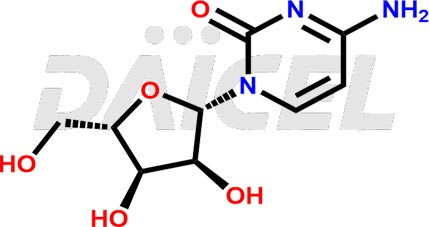
Cytidine
General Information
Cytidine Impurities and Cytidine
Daicel Pharma synthesizes Cytidine impurities of exceptional quality, such as Cytidine 2-Ethylbutyl Impurity (R-Isomer), Cytidine 2-Ethylbutyl Impurity (S-Isomer), Cytidine 2-Ethylbutyl Sesamol Impurity (R-Isomer), Cytidine 2-Ethylbutyl sesamol Impurity (S-Isomer), Cytidine Isopropyl Impurity, Cytidine Isopropyl Impurity (R-Isomer), Cytidine Isopropyl Impurity (S-Isomer) and L-Cytidine. These impurities are crucial to assess the purity, reliability, and safety of Cytidine, an active pharmaceutical ingredient. Besides, Daicel Pharma provides custom synthesis of Cytidine impurities to meet clients’ demands for delivery worldwide.
Cytidine [CAS: 65-46-3] is a pyrimidine nucleoside. It comprises attaching cytosine to ribofuranose through a beta-N(1)-glycosidic bond. It is an RNA component and plays a role in various physiological processes.
Cytidine: Use and Commercial Availability
Cytidine treats neuropsychiatric impairments associated with cerebrovascular diseases, often in combination with uridine, to enhance therapeutic effects. It serves as a pyrimidine compound that can be incorporated into nucleic acids and also acts as a substrate for the salvage pathway of pyrimidine nucleotide synthesis. The enzyme CTP synthase 1 (CTPS1) helps form Cytidine triphosphate, a vital precursor for DNA, RNA, and phospholipids.
Cytidine Structure and Mechanism of Action 
The chemical name of Cytidine is 1-((2R,3R,4S,5R)-3,4-Dihydroxy-5-(hydroxymethyl)tetrahydrofuran-2-yl)-4-(amino)pyrimidin-2(1H)-one. Its chemical formula is C9H13N3O5, and its molecular weight is approximately 243.22 g/mol.
The mechanism of action of Cytidine is unknown.
Cytidine Impurities and Synthesis
Impurities in Cytidine can arise from various sources, including manufacturing1, raw materials, or degradation during storage. They can impact the purity and quality of Cytidine, potentially affecting its performance and safety. So, it is necessary to analyze and control these impurities. The common Cytidine impurities may include related substances, degradation products, and residual solvents. Analytical methods such as HPLC or LC help detect and quantify these impurities, ensuring that Cytidine meets the required quality standards for its intended use in research or pharmaceutical applications.
Daicel Pharma offers a Certificate of Analysis (CoA) for Cytidine impurity standards, such as Cytidine 2-Ethylbutyl Impurity (R-Isomer), Cytidine 2-Ethylbutyl Impurity (S-Isomer), Cytidine 2-Ethylbutyl Sesamol Impurity (R-Isomer), Cytidine 2-Ethylbutyl sesamol Impurity (S-Isomer), Cytidine Isopropyl Impurity, Cytidine Isopropyl Impurity (R-Isomer), Cytidine Isopropyl Impurity (S-Isomer) and L-Cytidine, generated from an analytical facility compliant with cGMP standards. The CoA includes a comprehensive characterization report comprising data from techniques like 1H NMR, 13C NMR, IR, MASS, and HPLC purity. Furthermore, on request, we give additional data like 13C-DEPT and CHN. Daicel Pharma can synthesize unknown Cytidine impurities or degradation products. A complete characterization report accompanies every delivery.
References
FAQ's
Frequently Asked Questions
How are Cytidine impurities identified during analysis?
Cytidine impurities are identified through comparison with reference standards, matching the retention time in chromatographic techniques, spectral analysis (such as UV, IR, or NMR), and other suitable analytical methods.
Can Cytidine impurities affect the bioavailability of the drug?
Yes, certain impurities in Cytidine can potentially impact its bioavailability. They may interfere with drug absorption, metabolism, or distribution, causing variations in drug concentration and efficacy.
Which solvent helps in the analysis of Cytidine impurities?
Methanol is a solvent used for analyzing many impurities in Cytidine.
What are the temperature conditions required to store Cytidine impurities?
Cytidine impurities are stored at a controlled room temperature between 2-8 °C or as indicated on the Certificate of Analysis (CoA).
Note: Products protected by valid patents by a manufacturer are not offered for sale in countries having patent protection. The sale of such products constitutes a patent infringement, and its liability is at the buyer's risk.